|
Listen while working
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
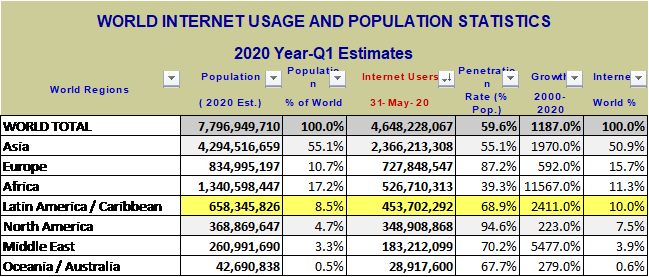
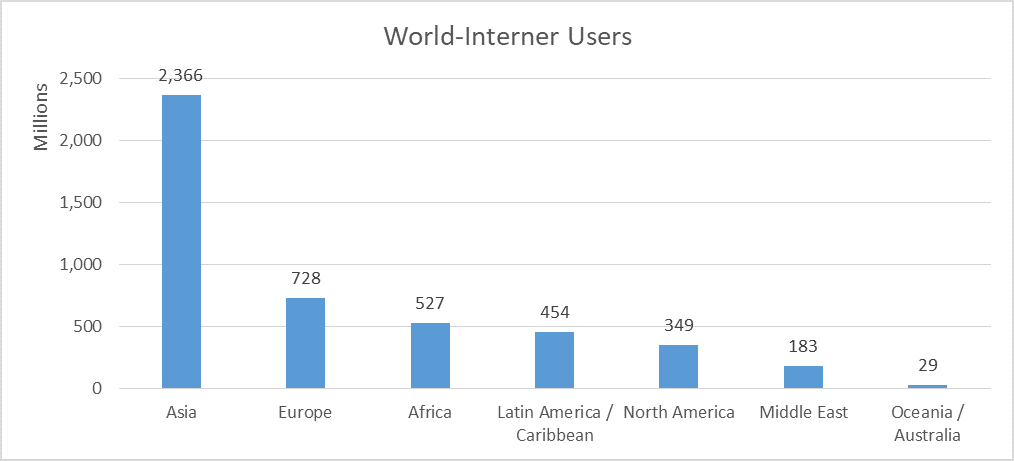
Internet use has increased exponentially in recent years, being more common every day. Worldwide, more than 7.8 billion people have access to the Internet, which is equivalent to 59.6% of the world population. Social media user worldwide are 3.45 billion. YouTube has 1.8 billion unique monthly visitors. There are now more than 2.5 billion active gamers around the world. That’s a billion more than just five years ago. In 2020, populations in game worlds will increase as the global population becomes more comfortable with gaming. With development of newer technology for fast speed and spread of internet coverage to farthest of areas.
While the internet is a massive source of information with 474,000 tweets, 400 hours of videos being watched by 4,333,560 videos each minute, over 69 million post each minute on Instagram, the time spent on internet is increasing at an alarming rate.
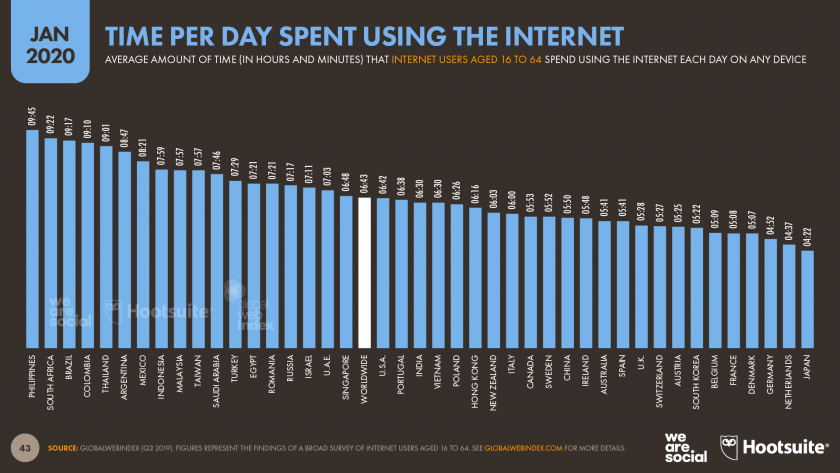
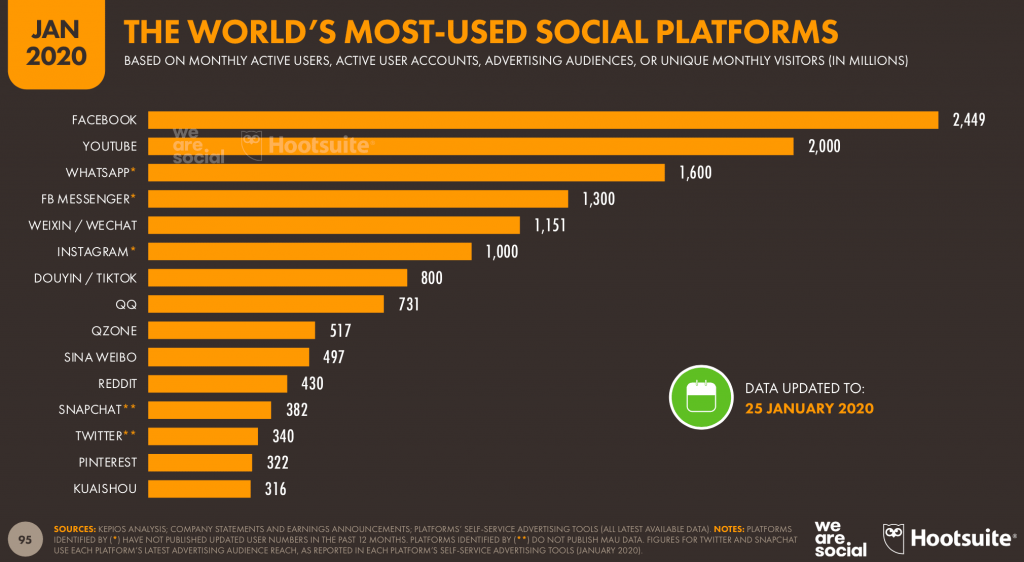
Data: smartinsights.com
Internet gaming disorder has been recognized by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) as a temporary disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) in 2013. The harmful consequences of excessive gaming is also recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO), and gaming disorder (GD) was included in their 11th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11) published in 2018.
Internet addiction disorder (IAD) commonly termed as compulsive internet use resulting in significant damage in an individual’s life over a long period of time. The growing interactions amid digital media and mental health have been under considerable research lately, and have spawned arguments from the medical, scientific and technological communities around the world.
Such disorders can be identified when an individual engages in online activities at the cost of fulfilling daily responsibilities or pursuing other interests, and without regard for the negative consequences.
The diagnostic criteria of Internet Gaming Disorder, including the following nine clinical symptoms explained in DSM-5
- Preoccupation with videogames
- Experiencing unpleasant symptoms when playing videogames
- The need to spend an increased amount of time involved in video games
- Failed attempts to control participation in videogames
- Losing interest in past hobbies and entertainment
- Continue to use videogames despite having knowledge of psychosocial problems
- Deceiving family members, therapists or others regarding the number of videogames
- Using videogames to escape or eliminate negative feelings
- Harm or lose relationships, work, or education or significant career opportunities
At this point of time, it is very difficult to recognize the importance of placing control measures over the use of internet, especially in teens or even younger ages, since our social values are changing drastically. However, the studies are evaluating the growing psychological problems related to excessive internet use.
Photo by Andrea Piacquadio from Pexels


